Why Does Heat Loss Occur in Buildings?
For a very long time, heat loss within buildings—the outcome of thermodynamic interactions when the heated inner and cold outer air collide—was considered as an unavoidable part of architectural construction.
Heat loss within a building is gauged using thermal transmittances. Heat transfer is also known as transfer efficiency or the R-value of a structure.
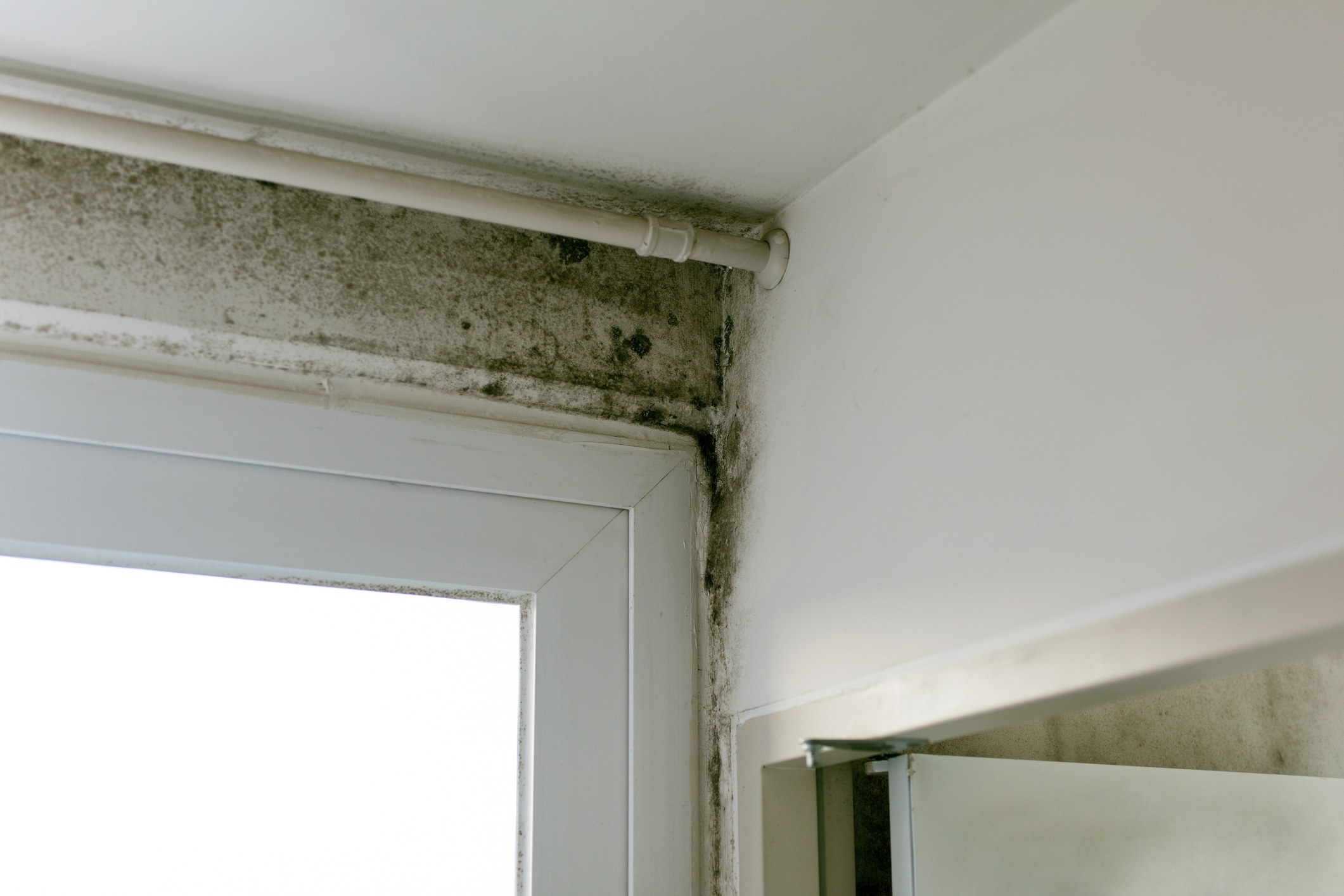
Older structures typically have far poorer heat loss ratings. This is due to the buildings’ propensity for draftiness, insufficient insulation, or mould growth brought on by an increase in the cold air that creates moisture as a result of temperature variations.
What Are Thermal Bridges and How Do They Form?
A thermal bridge is a region of a building or construction that is continuously penetrated by an element having a higher thermal conductivity. Particular locations of heat loss form thermal bridges.
Yet, the introduction of 3D modelling makes it possible to easily expose such thermal bridges, allowing any substantial causes to overall energy loss to be discovered.
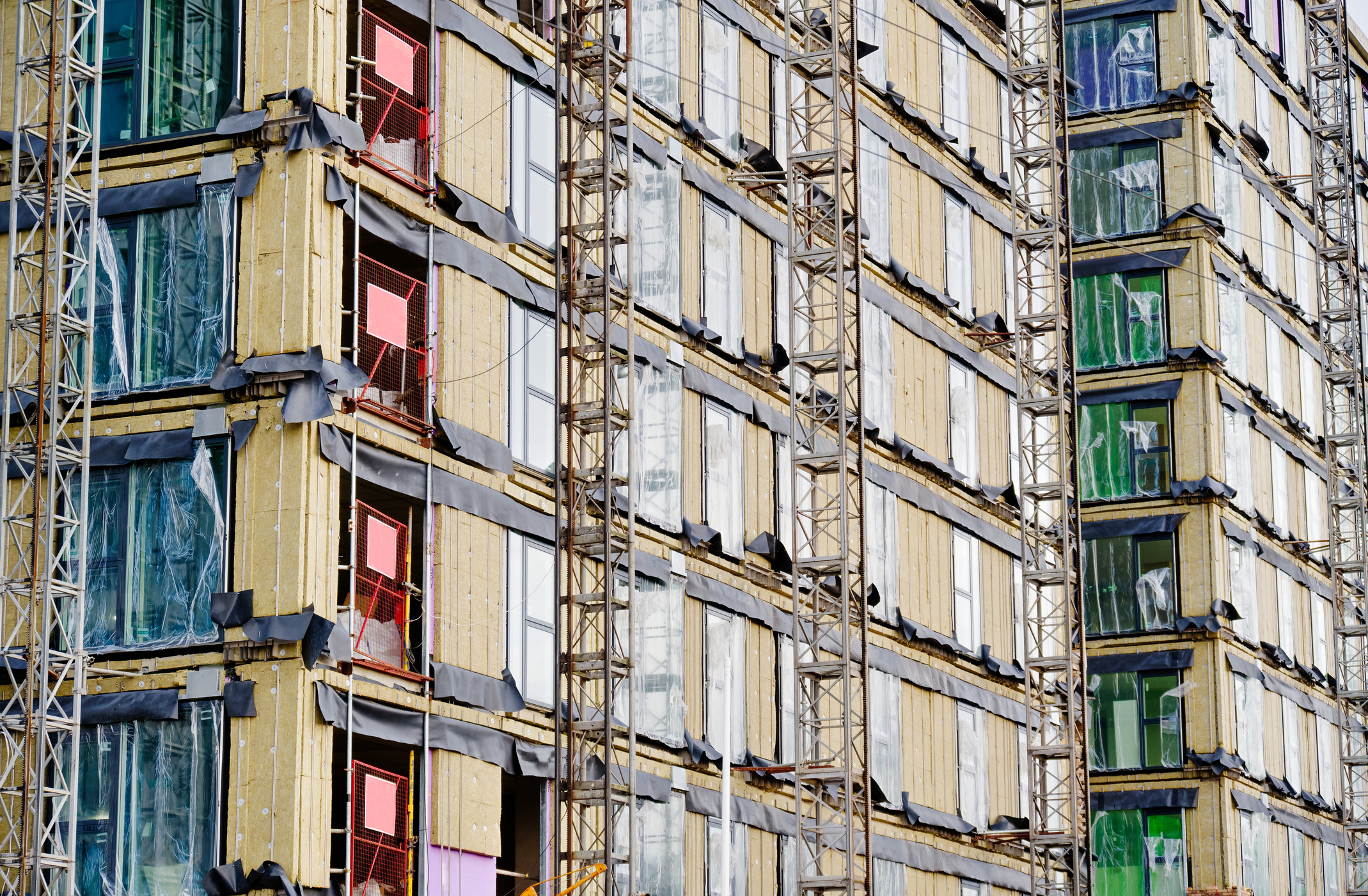
Many different applications that cause heat loss can be identified using 3D thermal modelling. The following assemblies may account for more than half of a building’s heat loss!
What Are the Missing Links in Continuous Insulation?
- Structural steel beams
In conventional structures, internal steel beams extend through the building’s floor slabs. In low temperature structures like freezer or cold storage rooms, thermal bridges form at the base of steel columns.
- Balconies and canopies
The most common interface details for structural framing are those that link to slab edges or spandrel beams on the interior side of the thermal envelope while passing through air barrier and insulation layers.
Thermal bridging at balcony and canopy connections can diminish a wall assembly’s R value by as much as 60%.
- Brick shelves
When there are non-continuous insulation features present, heat loss occurs at wall transitions and at the foundation perimeter, lowering the effective R value of the external wall.
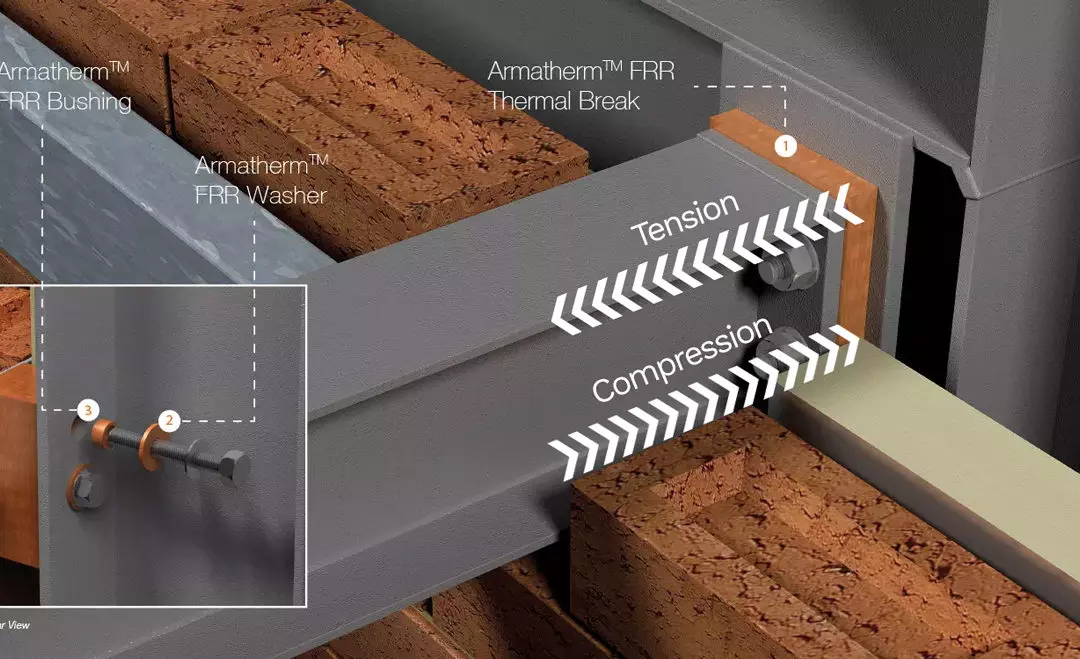
How Do Thermal Breaks Improve R Values and Reduce Energy Loss?
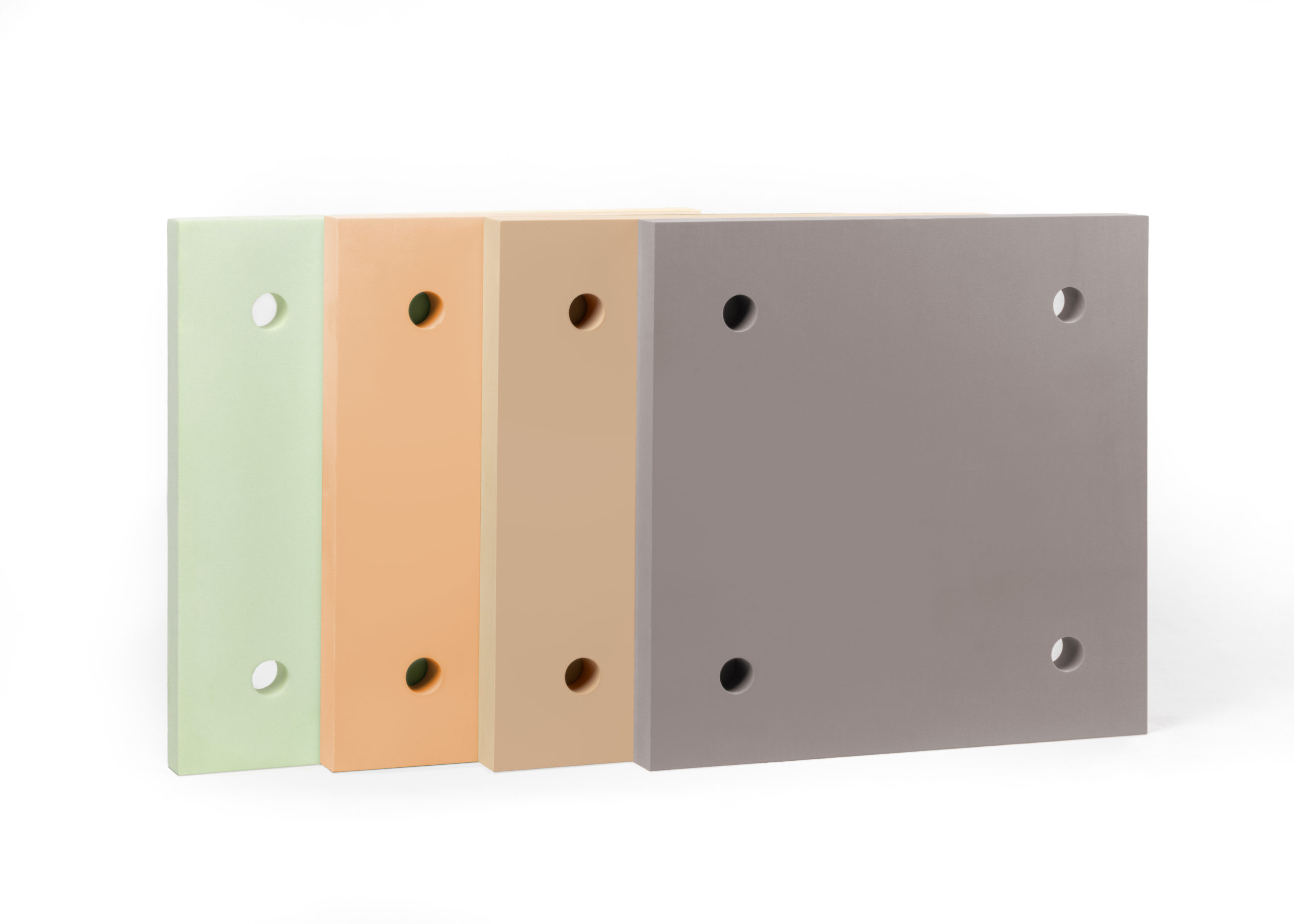
Using techniques where thermal breaks can insulate these crucial places and prevent, or reduce, thermal bridging is the key to raising the R value of structures and maintaining a well-insulated building.
What Solutions Does Armatherm Provide for Thermal Bridging?
Armatherm offers a comprehensive selection of solutions that are specifically designed to increase energy efficiency. We are a top provider of structural thermal break materials to the building sector.
Whenever there is a building envelope penetration, our thermal break solutions can be applied. By doing this, heat loss at places like balcony, canopy, parapet, masonry shelf angles, and cladding connections is effectively reduced.