The Role of High Performance Thermal Insulation in Structural Building Design
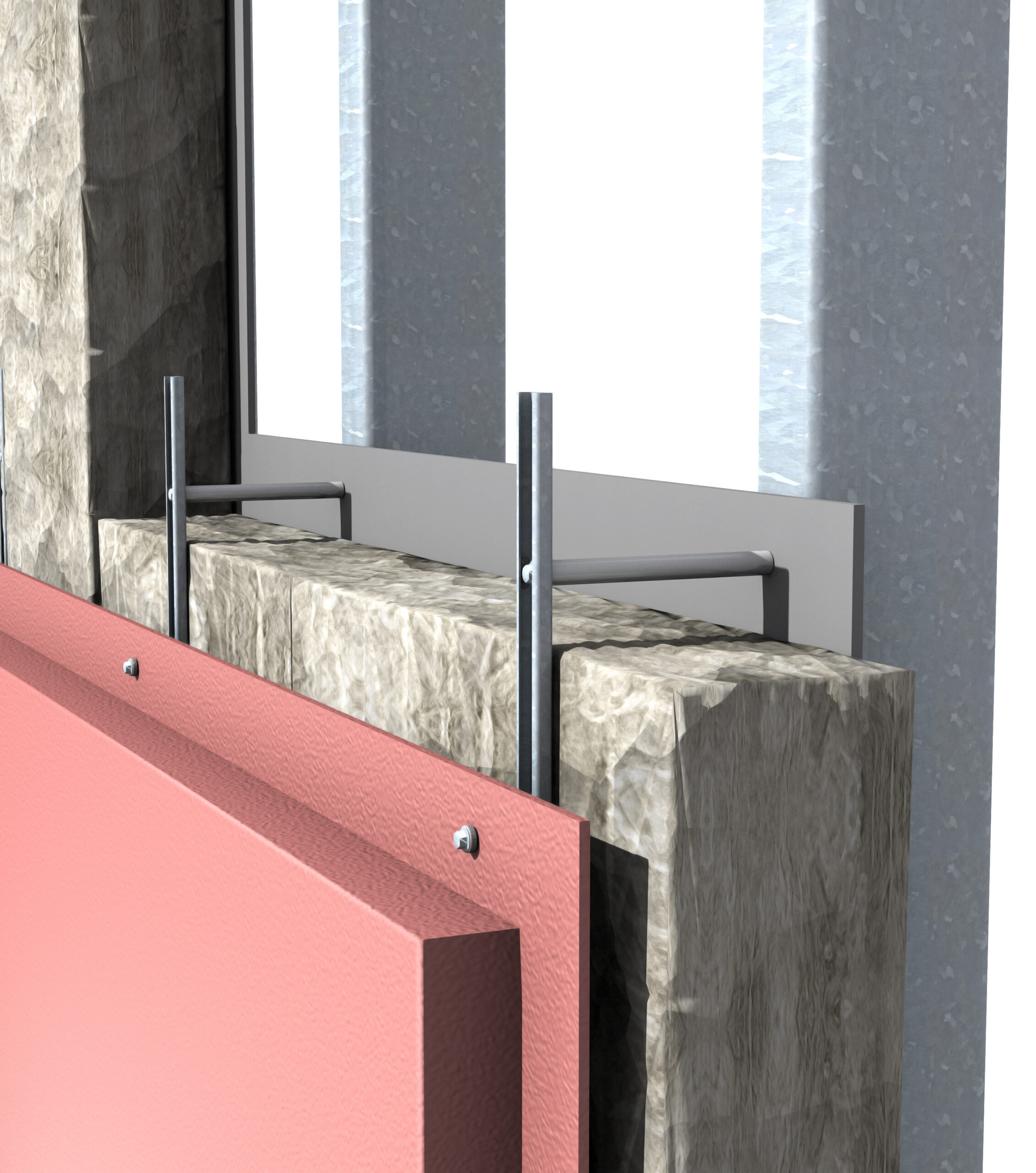
High performance thermal insulation plays a critical role in modern building design, especially where structural requirements and energy efficiency work in conjunction. For architects and engineers, insulation is no longer just about achieving target U-values, the specified materials must also support load-bearing elements, manage thermal movement and reduce heat loss at structural connections.
High Density and High Compressive Strength Insulation Explained
Two terms associated with high performance thermal insulation are high density and high compressive strength. While they are related, they are not interchangeable.
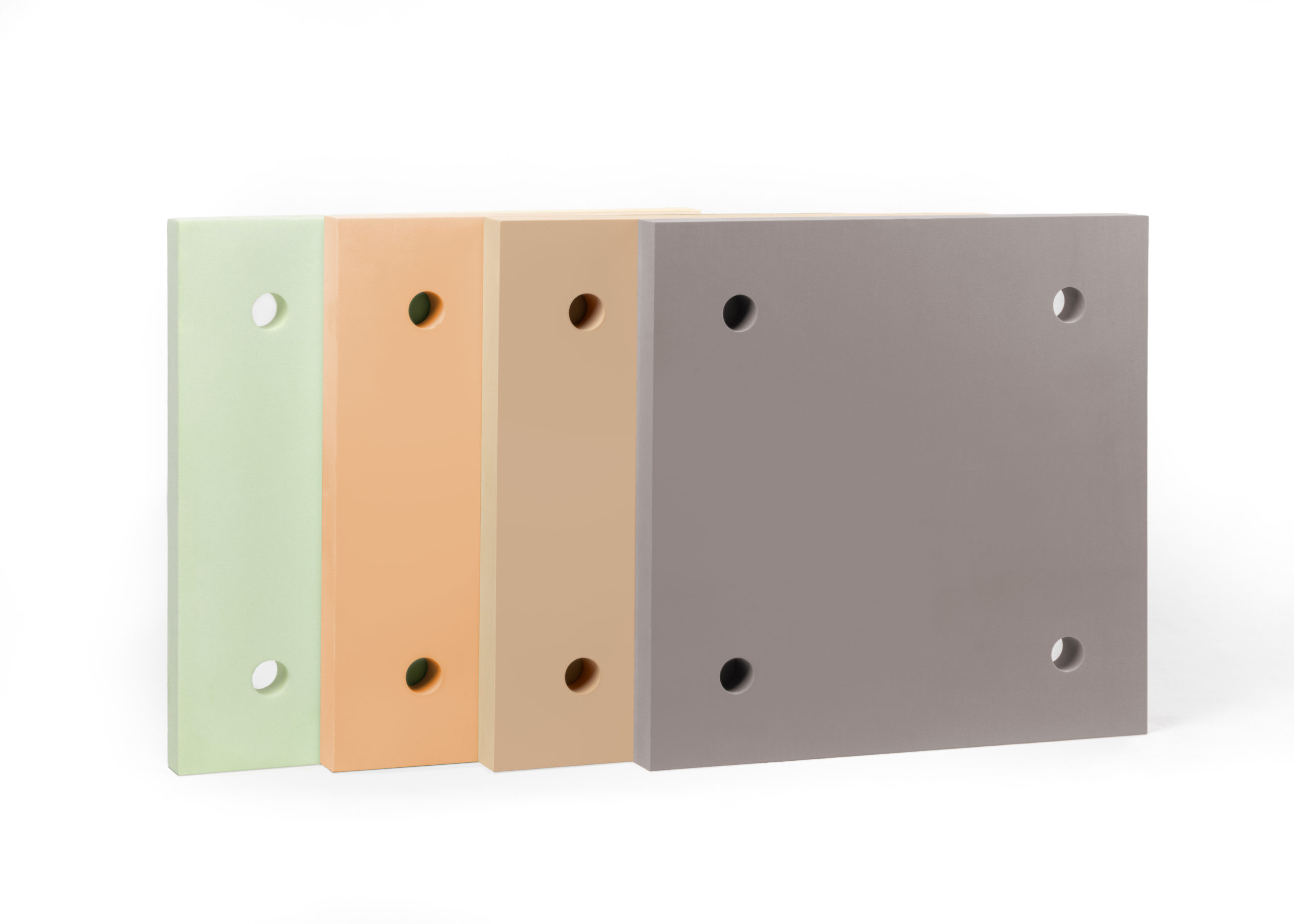
High density thermal insulation typically describes materials with a more compact internal structure. Increased density can improve durability and handling characteristics, but density alone does not define a material’s ability to support structural loads. Compressive strength must be assessed separately to ensure performance under load.
High compressive strength insulation, by contrast, is specifically engineered to withstand applied loads without excessive deformation.
This is essential in applications where insulation is required to:
- Support façade systems
- Sit beneath cladding rails or balcony connections
- Transfer loads at slab edges or structural penetrations
Specifying insulation without adequate compressive strength can result in long-term compression, thermal gaps and compromised performance. For this reason, compressive strength should always be assessed against actual project loads, rather than relying on generic or unsubstantiated claims.
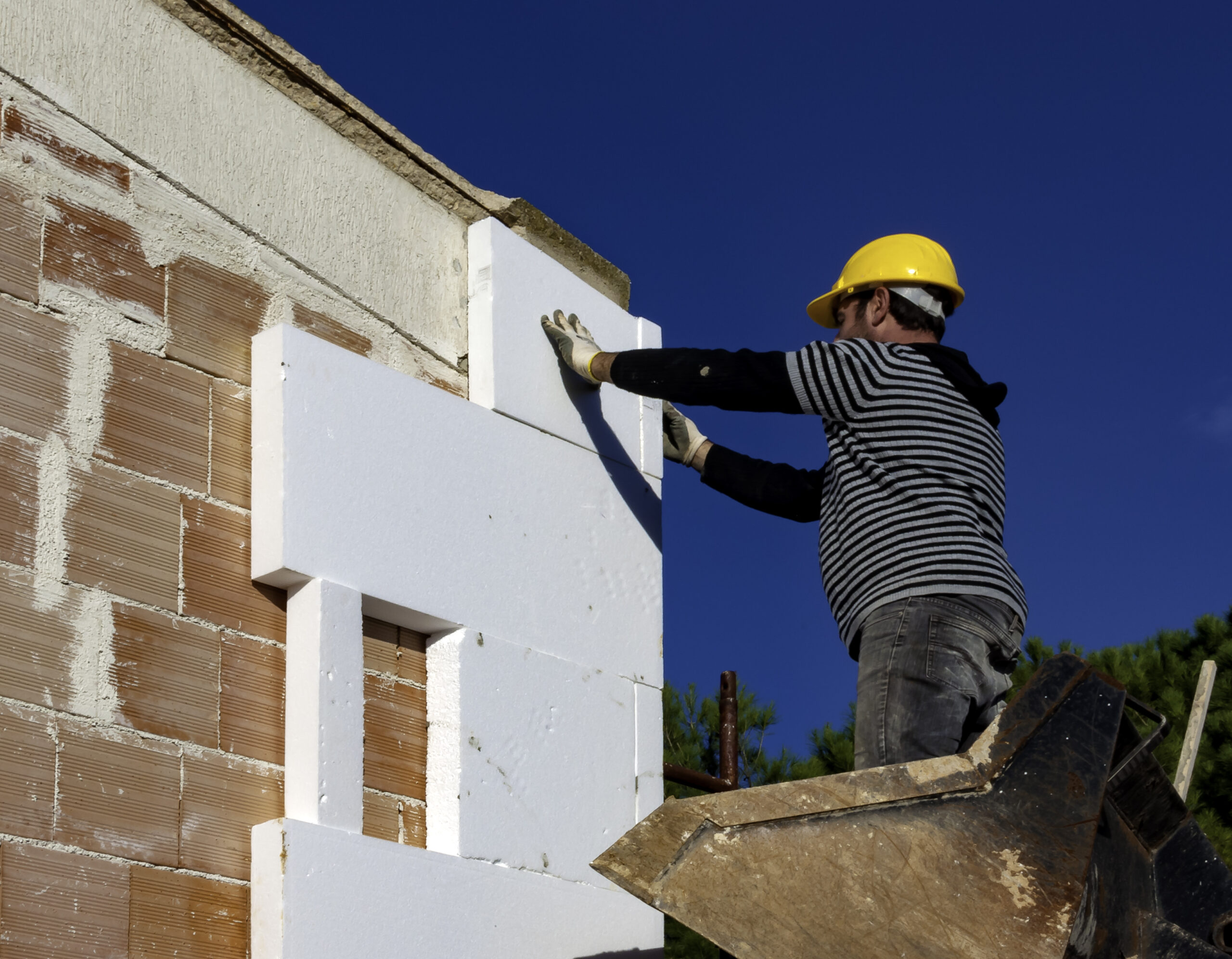
Using External Insulation to Reduce Thermal Bridging
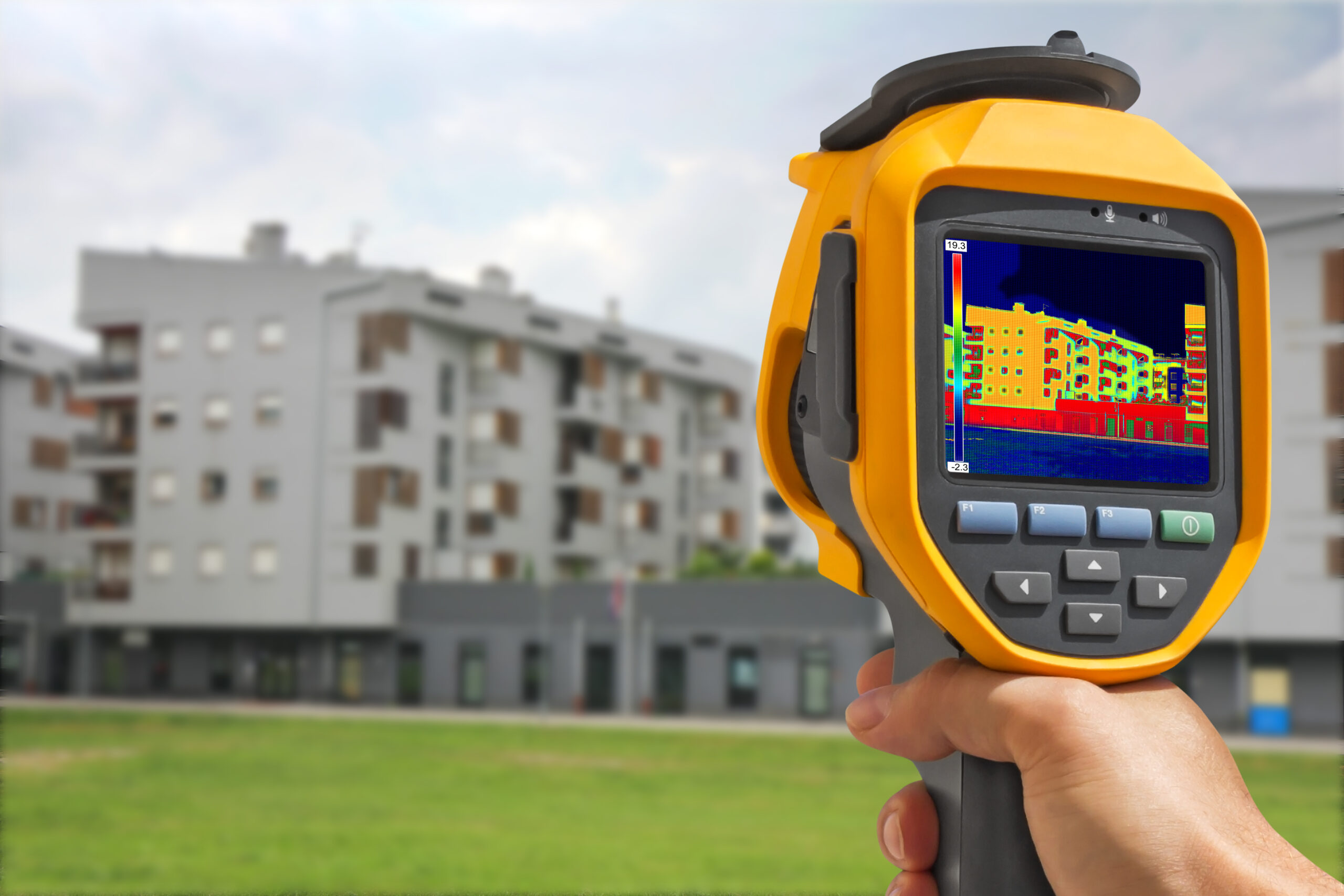
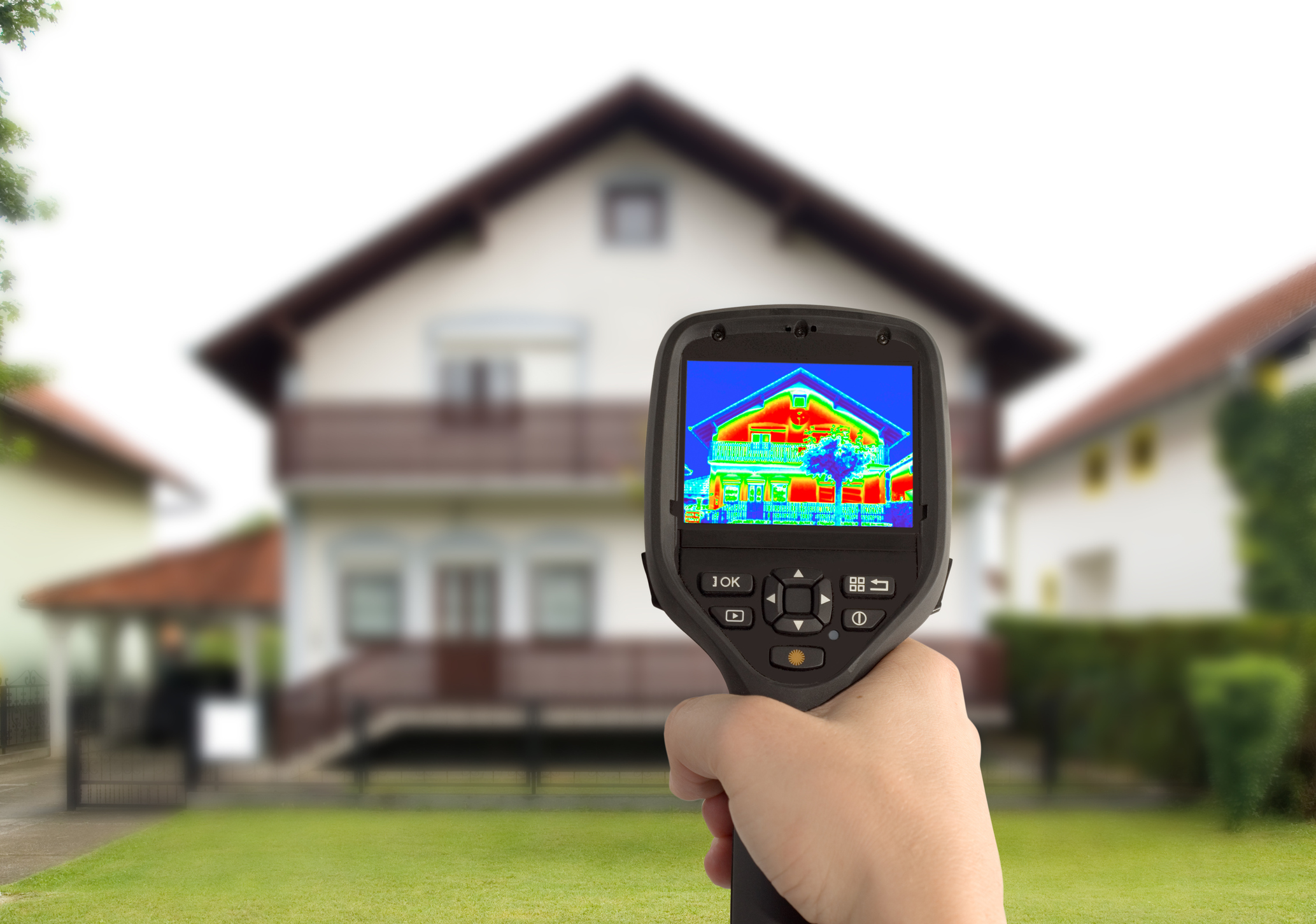
Thermal bridging occurs when conductive materials bypass insulation layers, allowing heat to escape more easily. Structural elements such as floor slabs, balconies, columns and steel connections are common sources of heat loss if not properly detailed.
External insulation strategies can significantly reduce thermal bridging by:
- Maintaining continuity of the thermal envelope
- Isolating structural elements from internal and external temperature differences
- Reducing surface condensation risk at connections
When combined with appropriate structural thermal breaks, external insulation systems help manage both heat flow and structural loads. Correct detailing is essential to ensure insulation continuity is not compromised by fixings, brackets or penetrations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is high performance thermal insulation?
High performance thermal insulation is insulation designed to maintain thermal efficiency while accommodating structural loads, fixings and junctions. It is typically used where standard insulation products would deform, degrade, or compromise thermal continuity.
When is high compressive strength insulation required?
High compressive strength insulation is required wherever insulation is subjected to permanent or variable loads, such as beneath cladding systems, at slab edges, or within load-bearing façade details. The specified compressive strength should always be matched to the calculated design loads.
How does external insulation reduce thermal bridging?
External insulation reduces thermal bridging by maintaining a continuous insulation layer around the building envelope. When combined with appropriate detailing and structural thermal breaks, it limits heat flow through structural elements that would otherwise bypass the insulation layer.